Carpal tunnel syndrome affects about 6% of the adults in the United States. (4) It causes pain, numbness and tingling, and can lead to nerve damage, and thus can be potentially dangerous. (9) Continue reading to learn more about carpal tunnel syndrome and how to manage it.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
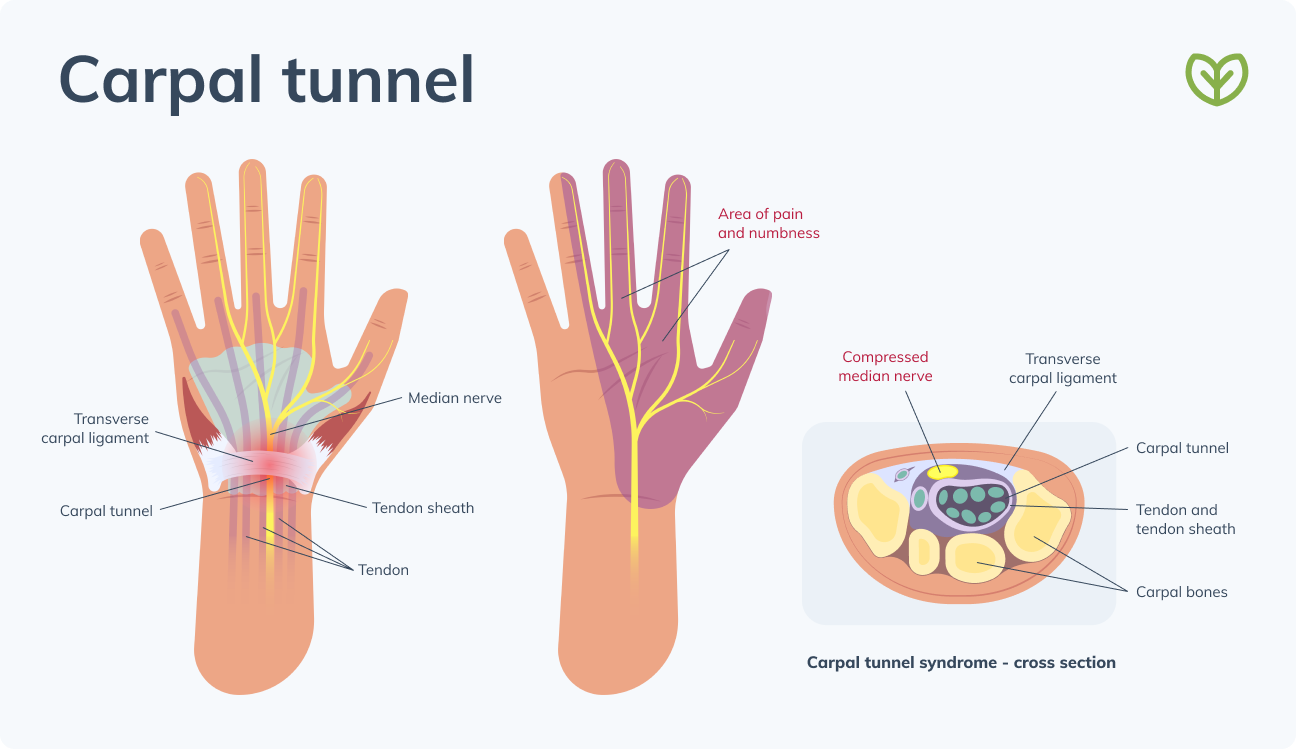
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the shoulder down the midline of the forearm and into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel is a narrow, passageway of ligaments and bones at the base of the hand.
The carpal tunnel houses the median nerve and the tendons that bend the fingers. The median nerve provides feeling to the palm side of the hand in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. It is also responsible for controlling some small muscles at the base of the thumb. (8) For this reason, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to numbness, tingling, weakness, and potential muscle damage in the hand and fingers. (12)
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is not usually associated with a problem in the median nerve itself. It is most commonly caused by a combination of factors that increase pressure on the median nerve and the tendons in the carpal tunnel. (8) Contributing factors that can cause carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Forceful movements of the wrist, such as hammering
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Repetative movements of the of the wrist, such as typing
- Use of hand-held vibratory tools, such as power drills
- Wrist injuries, such as fractures or sprains (8)(10)
Risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome
Women are usually more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than men. Additionally, individuals with diabetes may be more prone to carpal tunnel syndrome as diabetes increases the risk of nerve injury. (3)
Risk factors that increase your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome due to excess inflammation or fluid include:
- Congestive heart failure
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypopituitarism
- Kidney failure
- Menopause
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Use of oral contraceptives (5)(8)
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome can include:
- Dropping objects when gripping them
- Difficulty with fine finger movements in one or both hands
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index, middle finger, and ring finger
- Numbness or tingling in the palm
- Muscle loss under the thumb (in advanced or long-term cases)
- Pain in the hand or in the wrist that extends to the elbow
- Weak grip
- Weakness in one or both hands (12)
How is carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosed?
In order to determine if you have carpal tunnel syndrome your practitioner might:
- Conduct a physical examination of the hands, arms, shoulders, and neck to help determine if your complaints are related to daily activities or to an underlying disorder.
- Order routine laboratory tests and X-rays to rule out fractures, arthritis, and nerve-damaging diseases such as diabetes. (7)(8)
There are also some specific tests your practitioner may conduct in order to determine if you have carpal tunnel syndrome. These include:
- Electromyography: This involves a fine needle being inserted into a muscle. Electrical activity is then viewed on a screen to determine if there is damage to the median nerve.
- Nerve conduction studies: These types of tests involve electrodes being placed on the hand and the wrist. The electrodes give small electric shocks and then the speed with which the nerves transmit impulses is measured.
- The Tinel test: This test involves the practitioner tapping or applying pressure to the median nerve to determine if the added compression causes symptoms.
- The Phalen, or wrist-flexion test: This test involves having the person hold their forearms upright by pointing the fingers down and pressing the backs of the hands together. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be diagnosed if the positioning of the hands triggers one or more symptoms.
- Ultrasound imaging: This can be used to view the size of the median nerve in order to determine if there are any abnormalities. (7)(8)
How to manage carpal tunnel syndrome
The management of carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the condition. Most mild cases can be managed by lifestyle interventions. However, in some severe cases, surgery may be required. (11)
Lifestyle interventions that can help in the management of mild cases of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Avoiding sleeping on the wrists to prevent further compression of the median nerve
- Having an ergonomic desk set up, ensuring the keyboard and mouse are not pointing upwards while typing
- Using either warm or cold compresses to reduce pain and inflammation
- Using cushioned ergonomic keyboards and mouses when working at the computer
- Wearing wrist splints while sleeping (5)(11)(12)

Carpal tunnel syndrome exercises
The carpal tunnel exercises described below can help reduce the pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. As a result, they can help manage carpal tunnel syndrome and relieve symptoms. Individuals who do not have carpal tunnel syndrome but are at risk may also benefit from thesehome exercises. (2)
Exercise 1: Wrist extension stretch
To perform the wrist extension stretch,
- Extend your arm in front of you as though you are signaling someone to stop.
- With your other hand, gently pull your palm back towards you until you feel a mild to moderate stretch on the inside of your forearm.
- Hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat with the other arm if you’re experiencing carpal tunnel in both hands.
- Repeat for two to four sets. (2)(6)

Exercise 2: Wrist flexion stretch
To perform the wrist flexion stretch:
- Extend your arm in front of you with your palm facing down.
- Gently bend your wrist, pointing your fingers to the floor.
- With your other hand, gently pull your hand towards you until you feel a mild to moderate stretch on the outside of your forearm.
- Hold for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat with the other arm if you’re experiencing carpal tunnel in both hands.
- Repeat for two to four sets. (2)(6)

Exercise 3: Prayer stretch
To perform the prayer stretch:
- Start by putting your palms together in front of your chest, slightly below your chin.
- Slowly lower your hands towards your belly button, while keeping your palms together and hands close to your stomach, until you feel a mild to moderate stretch on the underside of your forearms.
- Hold 15 to 30 seconds.
- Repeat for two to four sets. (2)(6)

The bottom line
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, the nerve that runs from the shoulder down the midline of the forearm and into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. The median nerve is responsible for conducting feeling to the palm side of the hand including the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. Carpal tunnel syndrome can cause numbness, tingling, and pain, as well as possible nerve damage if left untreated.
CTS can typically be managed with lifestyle modifications and wrist exercises. However, in some severe cases, surgery may be required. Speak to your practitioner if you believe you may have CTS in order to safely and effectively manage the condition.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Therapeutic Exercises for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Ortho Info. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/globalassets/pdfs/a00789_therapeutic-exercise-program-for-carpal-tunnel_final.pdf
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2018, December). Therapeutic Exercise Program for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. OrthoInfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/recovery/carpal-tunnel-syndrome-therapeutic-exercise-program/
- Becker, J., Nora, D. B., Gomes, I., Stringari, F. F., Seitensus, R., Panosso, J. S., & Ehlers, J. A. C. (2002). An evaluation of gender, obesity, age and diabetes mellitus as risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome. Clinical Neurophysiology, 113(9), 1429–1434.
- Cestia, K. E. L. (2011, April 15). Carpal tunnel syndrome. American Family Physician. https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/0415/p952.html#:%7E:text=Carpal%20tunnel%20syndrome%20is%20the,%2C%20certain%20diseases%2C%20and%20pregnancy
- Genova, A., Dix, O., Saefan, A., Thakur, M., & Hassan, A. (2020). Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Literature. Cureus.
- Health Wise Alberta. (2020, November 16). Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Exercises. MyHealth Alberta. https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=ad1506
- Keith, M. W., Masear, V., Chung, K., Maupin, K., Andary, M., Amadio, P. C., Barth, R. W., Watters, W. C., Goldberg, M. J., Haralson, R. H., Turkelson, C. M., & Wies, J. L. (2009). Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 17(6), 389–396.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. NIH. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Carpal-Tunnel-Syndrome-Fact-Sheet
- Padua, L., Coraci, D., Erra, C., Pazzaglia, C., Paolasso, I., Loreti, C., Caliandro, P., & Hobson-Webb, L. D. (2016). Carpal tunnel syndrome: clinical features, diagnosis, and management. The Lancet Neurology, 15(12), 1273–1284.
- Palmer, K. T. (2011). Carpal tunnel syndrome: The role of occupational factors. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology, 25(1), 15–29.
- Shi, Q., & MacDermid, J. C. (2011). Is surgical intervention more effective than non-surgical treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome? a systematic review. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 6(1), 17.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Carpal tunnel syndrome. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000433.htm





